
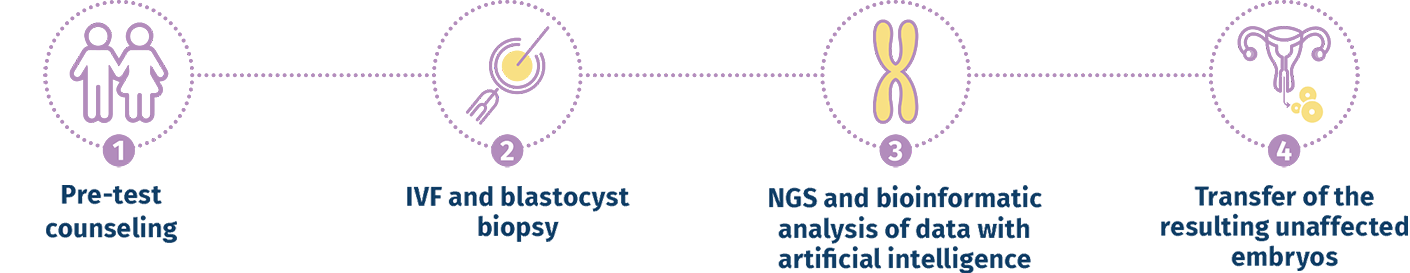
Preimplantation genetic testing for chromosomal aneuploidy (PGT-A)

Preimplantation genetic testing for chromosomal aneuploidy (PGT-A) is a technique used in conjunction with In- Vitro fertilization (IVF) to detect embryos with extra or missing chromosomes (aneuploidy). An extra chromosome is known as a "trisomy" and a missing chromosome is known as "monosomy".
Through PGT-A, the selection of embryos to be transferred to the uterus is based not only on a morphological evaluation but also on the related chromosomal ploidy, which reflects their possibility of giving rise to an ongoing pregnancy.
Embryos that are affected by certain chromosomal conditions can lead to failure of implantation, pregnancy loss, or result in the birth of a child with physical and/or mental problems. The purpose of PGT-A is to help prevent adverse outcomes by identifying affected embryos in the laboratory and preventing them from being transferred into the uterus.
PGT-A can help in the selection of chromosomally normal embryos for transfer in order to increase the chance of pregnancy, reduce the chance of miscarriage, and reduce the chance of children born with medical conditions.
GROUNDBREAKING TECHNOLOGIES
AND HIGH QUALITY STANDARDS

A genetic test designed to identify in embryos chromosomal aneuploidy and unbalanced structural abnormalities
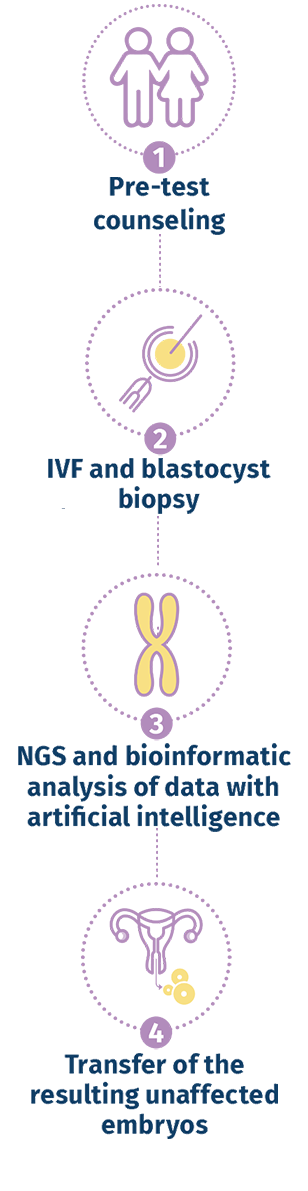


 Italiano
Italiano English
English